Activity against a number of parasites has also been demonstrated Its cellular pharmacokinetics, postantibiotic effect and interactions with host Spiramycin is a 16memberedring macrolide with an antibacterial spectrum characteristic of this class of drugs and including Gramnegative and Grampositive cocci, Parvobacteriaceae and some intracellular organisms;Molecular structure The molecular structure is based on structures generated from information available in ECHA's databases If generated, an InChI string will also be generated and made available for searching This information is only displayed if the substance is welldefined, its identity is not claimed confidential and there is sufficient information available in ECHA's databases for ECHA's algorithms to generate a molecular structure
Spiramycin New Drug Approvals
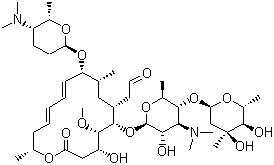
Spiramycin structure and chemical name
Spiramycin structure and chemical name-Spiramycin II is a macrolide antibiotic produced by various Streptomyces species It has a role as an antibacterial drug, an antimicrobial agent and a bacterial metabolite It is an aldehyde, a disaccharide derivative, an ether, a macrolide, a tertiary amino compound and an acetate esterFind and related products for scientific research at MilliporeSigma




Epa1 Levoisovalerylspiramycin Iii And Preparations Preparation Methods And Uses Thereof Google Patents
Spiramycin, a widely used veterinary macrolide antibiotic, was found at traceable levels (nanograms per litre range) in Po River water (NItaly) The aqueous environmental fate of this antibiotic compound was studied through drug decomposition, the identification of the main and secondary transformation products (TPs), assessment of mineralisation and the investigationUsing a structure estimation method based on molecular connectivity indices(1), the Koc of spiramycin can be estimated to be 140(SRC) According to a classification scheme(2), this estimated Koc value suggests that spiramycin is expected to have high mobility in soil Estimated pKa values of spiramycin are 7 and 928(3), indicating that this compound will exist almostSpiramycin was effective against a number of such strains in vivo, but erythromycin had little effect against these infections Investigation into the distribution of the antibiotics in the serum and tissues of mice showed that spiramycin was maintained in tissues (lung, liver, kidney, spleen and heart) at higher concentrations and for a longer period than erythromycin, although erythromycin
Monoisotopic mass Da;Biochem/physiol Actions Spiramycin is a 16membered ring macrolide antibiotic from Streptomyces ambofaciens It inhibits bacterial protein synthesis at the level of peptidytRNA dissociation from ribosomes It is mainly used against Grampositive bacteriaAcetylspiramycin C45H76N2O15 CID structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological activities, safety/hazards/toxicity information, supplier lists, and more
Structure, properties, spectra, suppliers and links for Spiramycin I An antibiotic used for the treatment and control of a number of bacterial and mycoplasmal infections in animals and also used as a growth promotor Availability status Introduction & key dates 00, Europe Examples of species treated Poultry, Sheep, Cattle, Pigs, Cats, Dogs Chemical structure IsomerismSpiramycin, hexanedioate (11) (salt) The 'Substance identity' section is calculated from substance identification information from all ECHA databases The substance identifiers displayed in the InfoCard are the best available substance name, EC number, CAS number and/or the molecular and structural formulas Some substance identifiers may




Spiramycin Iii Cas 52 7



Spiramycin Adipate C49h84n2o18 Pubchem
Chemical Structure and Safety of Spiramycin Jacques Descotes 1 Drug Investigation volume 6, pages 43–48 (1993)Cite this article 29 Accesses 3 Citations Metrics details Summary Since the introduction of spiramycin, thousands of patients have been treated with the drug and few have developed severe adverse reactions Gastrointestinal disorders were usually mild andSpiramycin I Molecular Formula C 43 H 74 N 2 O 14;Were identified and their structure confirmed by mass spectrometry Residues of parent drug accounted for 04 mg/kg, while residues of spiramycin adducts with Lcysteine represented 105 mg/kg, and neospiramycin adducts with Lcysteine accounted for an additional 22 mg/kg of residues However, the transformation into cysteine compound is



Q Tbn And9gcth3d8x1nireuodgfhyz04qsitlwdy5u24hqn3wfh7gfdgiknay Usqp Cau



1
A macrolide antibiotic produced by Streptomyces ambofaciens The drug is effective against grampositive aerobic pathogens, N gonorrhoeae, and staphylococci It is used to treat infectionsCrystal structures of the Haloarcula marismortui large ribosomal subunit complexed with the 16membered macrolide antibiotics carbomycin A, spiramycin, and tylosin and a 15membered macrolide, azithromycin, show that they bind in the polypeptide exit tunnel adjacent to the peptidyl transferase center Their location suggests that they inhibit protein synthesis by blocking theAverage mass Da;



Spiramycin Adsorption Behavior On Activated Bentonite Activated Carbon And Natural Phosphate In Aqueous Solution Springerlink



Coa Of Spiramycin Certificate Of Analysis Abmole Bioscience
Spiramycin is a macrolide antibiotic and antiparasitic It is used to treat toxoplasmosis and various other infections of soft tissues Although used in Europe, Canada and Mexico, 1 spiramycin is still considered an experimental drug in the United States, but can sometimes be obtained by special permission from the FDA for toxoplasmosis in the first trimester of pregnancy 2Structure, properties, spectra, suppliers and links for spiramycin IIISpiramycin I ChEBI ID CHEBI Definition A macrolide antibiotic produced by various Streptomyces species that is used to treat toxoplasmosis and various other infections of soft tissues Stars This entity has been manually annotated by the ChEBI Team Secondary ChEBI IDs




Spiramycin Wikipedia



Rovamycin C43h74n2o14 Pubchem
Keyword 'spiramycin' Spiramycin Spiramycin Synonyms Formacidine, Spiramycin CAS Number EC NumberChemical structure macrolide Application Spiramycin is a macrolide antibiotic that is commonly used to treat infections of soft tissues It has been used to treat bronchopulmonary infections in adults and has been used to study septicemia in mice Biochem/physiol Actions Spiramycin is a 16membered ring macrolide antibiotic from Streptomyces ambofaciens It inhibits bacterialTo the Spiramycin residue monograph prepared by the 43rd meeting of the Committee and published in FAO Food and Nutrition Paper 41/7, Rome 1995 Introduction As the sponsor was unable to provide a validated chemical method for the analysis of spiramycin and neospiramycin residues in pig tissues to the 43rd JECFA meeting in 1994, it was not possible to estimate the




Chemical Structures Of Main Components Of Spiramycin And Its Related Download Scientific Diagram




Chemical Structures Of Main Components Of Spiramycin And Its Related Download Scientific Diagram
Tetrahydrofuranyl and tetrahydropyranyl derivatives of neospiramycin I at 3 and/or 4' position were synthesized In vitro and in vivo activities of these derivatives were correlated with the position and configuration of acetal groups The most effective derivative, 3a, 4'adiOtetrahydrofuranylneospiramycin I was comparable to spiramycin I Crystal structures of the Haloarcula marismortui large ribosomal subunit complexed with the 16membered macrolide antibiotics carbomycin A, spiramycin, and tylosin and a 15membered macrolide, azithromycin, show that they bind in the polypeptide exit tunnel adjacent to the peptidyl transferase center Their location suggests that they inhibit protein synthesis byCrystal structures of the Haloarcula marismortui large ribosomal subunit complexed with the 16membered macrolide antibiotics carbomycin A, spiramycin, and tylosin and a 15membered macrolide, azithromycin, show that they bind in the polypeptide exit tunnel adjacent to the peptidyl transferase center Their location suggests that they inhibit protein synthesis by blocking the



Spiramycin New Drug Approvals




Acetyl Spiramycin Spiramycin Adipate Spiramycin Base Manufacturers And Suppliers Price Fengchen
PLQDGTZICFBBSODPUAUXBSSAN Spiramycin adipate Similar structures search, synonyms, formulas, resource links, and other chemical informationSpiramycin II Molecular Formula C 45 H 76 N 2 O 15; As a member of the wwPDB, the RCSB PDB curates and annotates PDB data according to agreed upon standards The RCSB PDB also provides a variety of tools and resources Users can perform simple and advanced searches based on annotations relating to sequence, structure and function These molecules are visualized, downloaded, and analyzed by users who range from
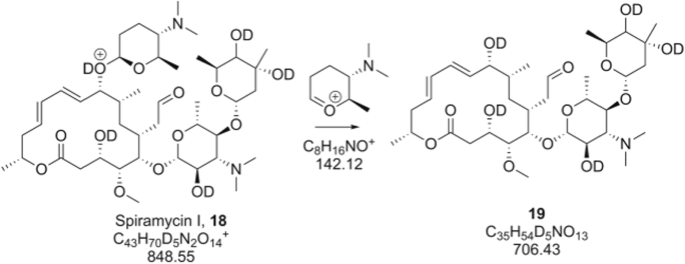



Structure Elucidation Of Macrolide Antibiotics Using Ms N Analysis And Deuterium Labelling Springerlink




Structure Activity Relationships Of Ketolides Vs Macrolides Douthwaite 01 Clinical Microbiology And Infection Wiley Online Library
CHEBI spiramycin II A macrolide antibiotic produced by various Streptomyces species This entity has been manually annotated by the ChEBI Team No supplier information found for this compound A molecular entity capable of accepting a hydron from a donor (Br o nsted acid) A drug used to treat or prevent bacterial infectionsSummarySince the introduction of spiramycin, thousands of patients have been treated with the drug and few have developed severe adverse reactions Gastrointestinal disorders were usually mild and transient, and allergic reactions were quite uncommon Liver injury was described only once and drug interactions have not been reported The safety profile of this 16membered lactoneDas Antibiotikum Spiromycin besitzt die chemische Summenformel C 43 H 74 N 2 O 14 Bei Zimmertemperatur liegt die Substanz als festes, kristallines Pulver vor In dieser Form besitzt einen leicht hygroskopischen Charakter, d h es zieht Wasser aus der Luft an In Wasser ist der Wirkstoff nur schwach löslich



Spiramycin I C43h74n2o14 Chemspider




Spiramycin I 50 5
Spiramycin is a 16membered ring macrolide (antibiotic) It was discovered in 1952 as a product of Streptomyces ambofaciens As a preparation for oral administration it has been used since 1955, in 1987 also the parenteral form was introduced into pr Read More Please waitSpiramycin U contains total 133 bond(s);Monoisotopic mass Da;




Spiramycin Formacidine Nsc Rovamycine Cas Number 8025 81 8 Cayman Chemical




Rcsb Pdb 5igz Macrolide 2 Phosphotransferase Type Ii Complex With Gdp And Spiramycin
Chemical structure and selected properties of spiramycin and metronidazole Physicochemical data from National Center for Biotechnology Information 51 and Kalhori 26 Stock solutions of both antibiotics were prepared at 100 mg L −1 in highpurity Milli Q water62 nonH bond(s), 4 multiple bond(s), 11 rotatable bond(s), 4 double bond(s), 3 sixmembered ring(s), 1 ester(s) (aliphatic), 1 aldehyde(s) (aliphatic), 2 tertiary amine(s) (aliphatic), 4 hydroxyl group(s), 3 secondary alcohol(s), 1 tertiary alcohol(s) and 7 ether(s) (aliphatic) Learn more about Spiramycin I chemical structure at MolInstinctsSpiramycin adipate C49H84N2O18 CID structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological activities, safety/hazards/toxicity information, supplier lists, and more




Chemical Structures Of Main Components Of Spiramycin And Its Related Download Scientific Diagram



Spiramycin 8025 81 8
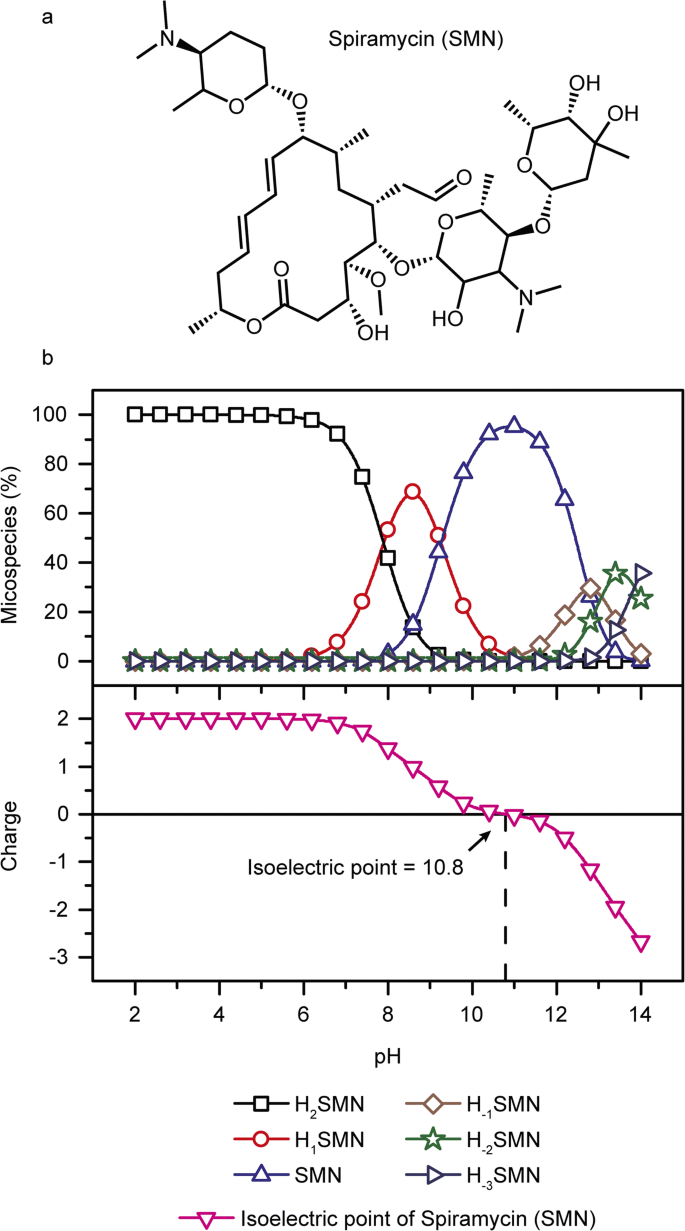
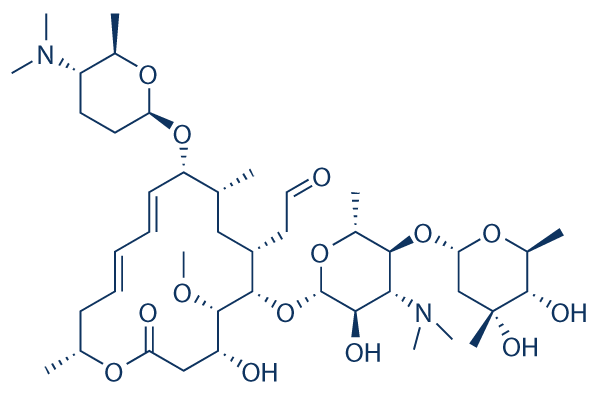
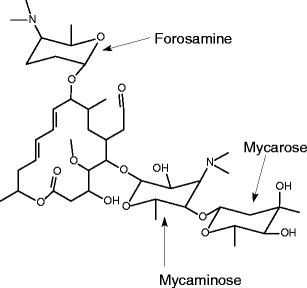
Average mass 50 Da;Spiramycin is a complex formed by three major components (I–III), which differ in the substituent at position 3 of the lactone nucleus The spiramycins are more stable than erythromycin A in an acidic medium Roxithromycin is highly stable at pH 42 (Figure 1414) Clarithromycin is 6Omethylerythromycin A, and the hydroxyl at position 11 remains free A degradation productSpiramycin Structure Close Systematic / IUPAC Name 2(4 R ,5 S ,6 S ,7 R ,9 R ,10 R ,11 E ,13 E ,16 R )6(2 S ,3 R ,4 R ,5 S ,6 R )5(2 S ,4 R ,5 S ,6 S )4,5Dihydroxy4,6dimethyloxan2yloxy4(dimethylamino)3hydroxy6methyloxan2yloxy10(2 S ,5 S ,6 R )5(dimethylamino)6methyloxan2yloxy4hydroxy5methoxy9,16dimethyl2oxo1
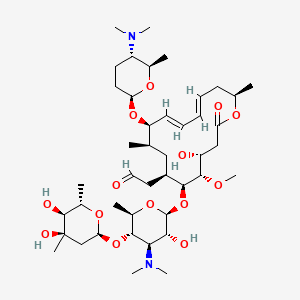



Spiramycin C43h74n2o14 Pubchem




Spiramycin Adipate Cas 680 55 7 Glentham Life Sciences
Spiramycin I contains total 136 bond(s); Both structural features seem to increase toxicity Removal of the nitro group leading to augmented toxicity was also confirmed through QSAR analysis of clothianidin and thiamethoxam and their transformation products The proposed structures corresponding to m/z = 247 and 263 of thiametoxam serve as examples Unfortunately, no suitable QSAR model could be used forWe are Spiramycin CAS suppliers and specialize ,,, etc




A Chemical Structure Of Spiramycin Pk 7 9 B Dose Dependent Download Scientific Diagram



1
62 nonH bond(s), 4 multiple bond(s), 10 rotatable bond(s), 4 double bond(s), 3 sixmembered ring(s), 1 ester(s) (aliphatic), 1 aldehyde(s) (aliphatic), 1 tertiary amine(s) (aliphatic), 6 hydroxyl group(s), 4 secondary alcohol(s), 2 tertiary alcohol(s) and 7 ether(s) (aliphatic) Learn more about Spiramycin U chemical structure at MolInstincts




Spiramycin I D3 C43h74n2o14 Pubchem



Structures Of Spiramycins Neospiramycins Spiramycins U And S And Download Scientific Diagram




Acetyl Spiramycin Biochemical Mybiosource




Chemical Structure Of Spiramycin With Labels Download Scientific Diagram
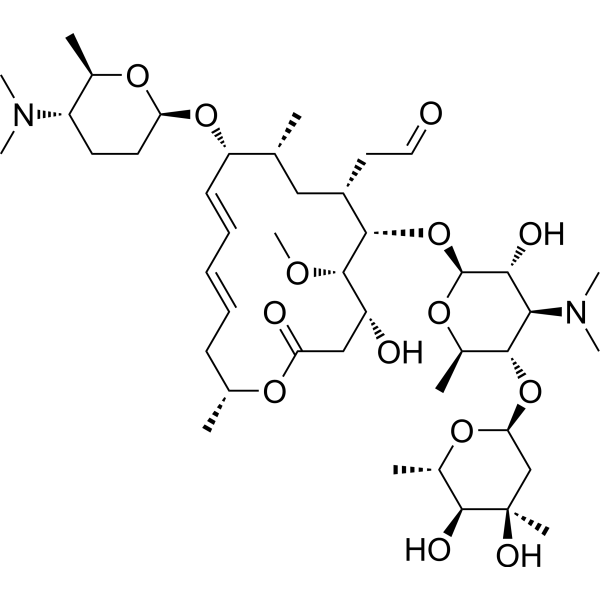



Spiramycin Rovamycin Antibiotic Medchemexpress
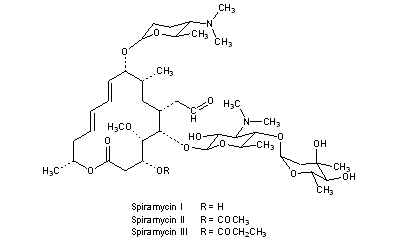



Spiramycin
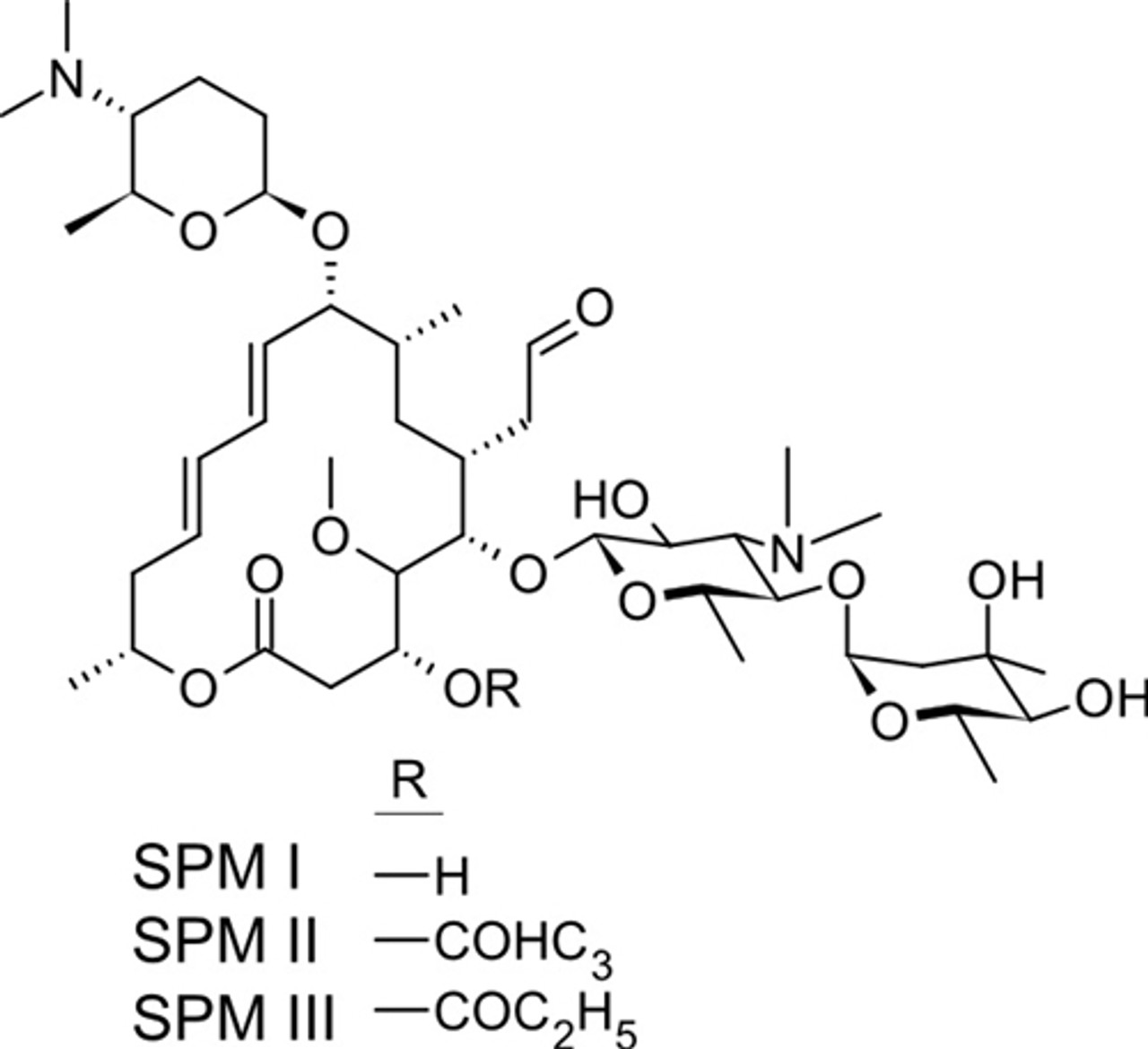



Spiramycin Toku E




Spiramycin Ii



Spiramycin Supplier Casno 8025 81 8




Antibacterial Inactivation Of Spiramycin After Titanium Dioxide Photocatalytic Treatment Sciencedirect




Epa1 Levoisovalerylspiramycin Iii And Preparations Preparation Methods And Uses Thereof Google Patents




Spiramycin Structure C43h74n2o14 Over 100 Million Chemical Compounds Mol Instincts




Spiramycin Iii Cas 52 7 Iii Antibiotic Medkoo




Rapid Thermal Acid Hydrolysis Of Spiramycin By Silicotungstic Acid Under Microwave Irradiation Sciencedirect




Spiramycin I D3




Spiramycin Adipate Cas 680 55 7 Chemsrc
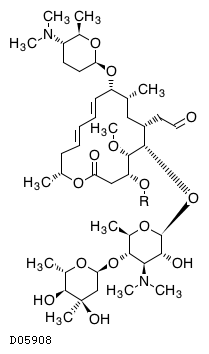



Kegg Drug Spiramycin
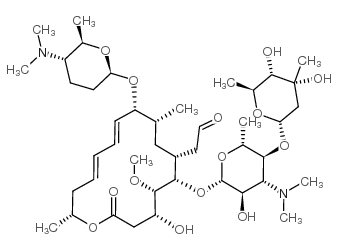



Spiramycin I Cas 50 5 Chemsrc




Spiramycin Ii




Spiramycin 8025 81 8



Spiramycin スピラマイシン Drug Approvals International
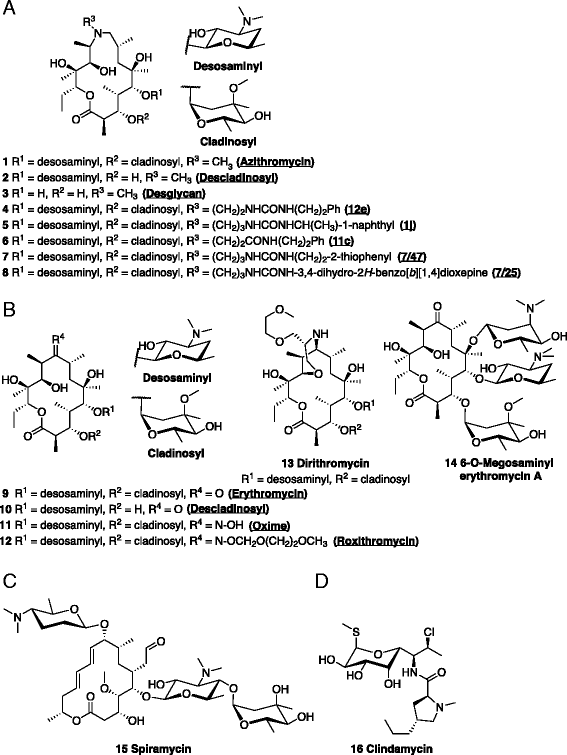



Macrolides Rapidly Inhibit Red Blood Cell Invasion By The Human Malaria Parasite Plasmodium Falciparum Bmc Biology Full Text




Rovamycin 3 000 000 Iu 10 Pcs
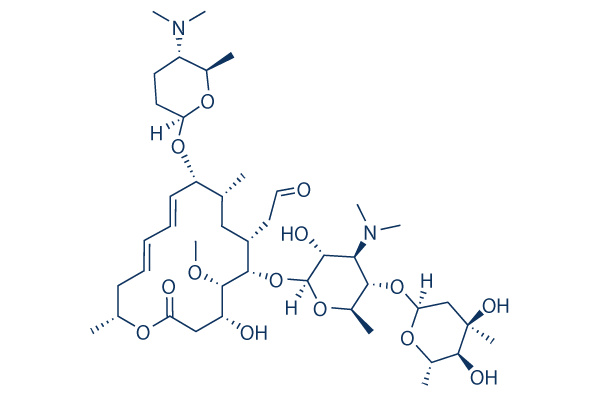



Spiramycin I 99 Hplc Selleck Antibiotics Chemical Qcfile
/D218B7AA3AA73D1B802585F8006742F1/$file/AS16859_structure.png)



Spiramycin I 50 5 Carbosynth Product
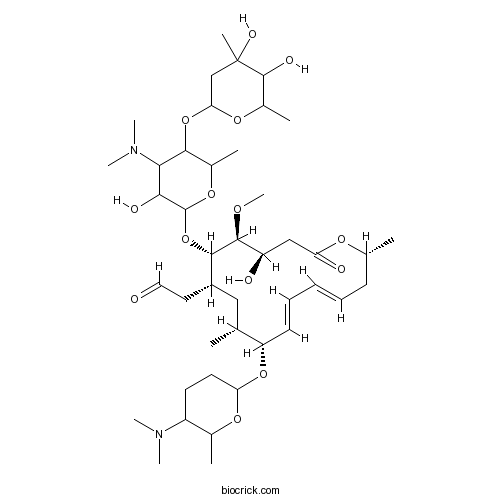



Spiramycin Cas 8025 81 8 High Purity Manufacturer Biocrick
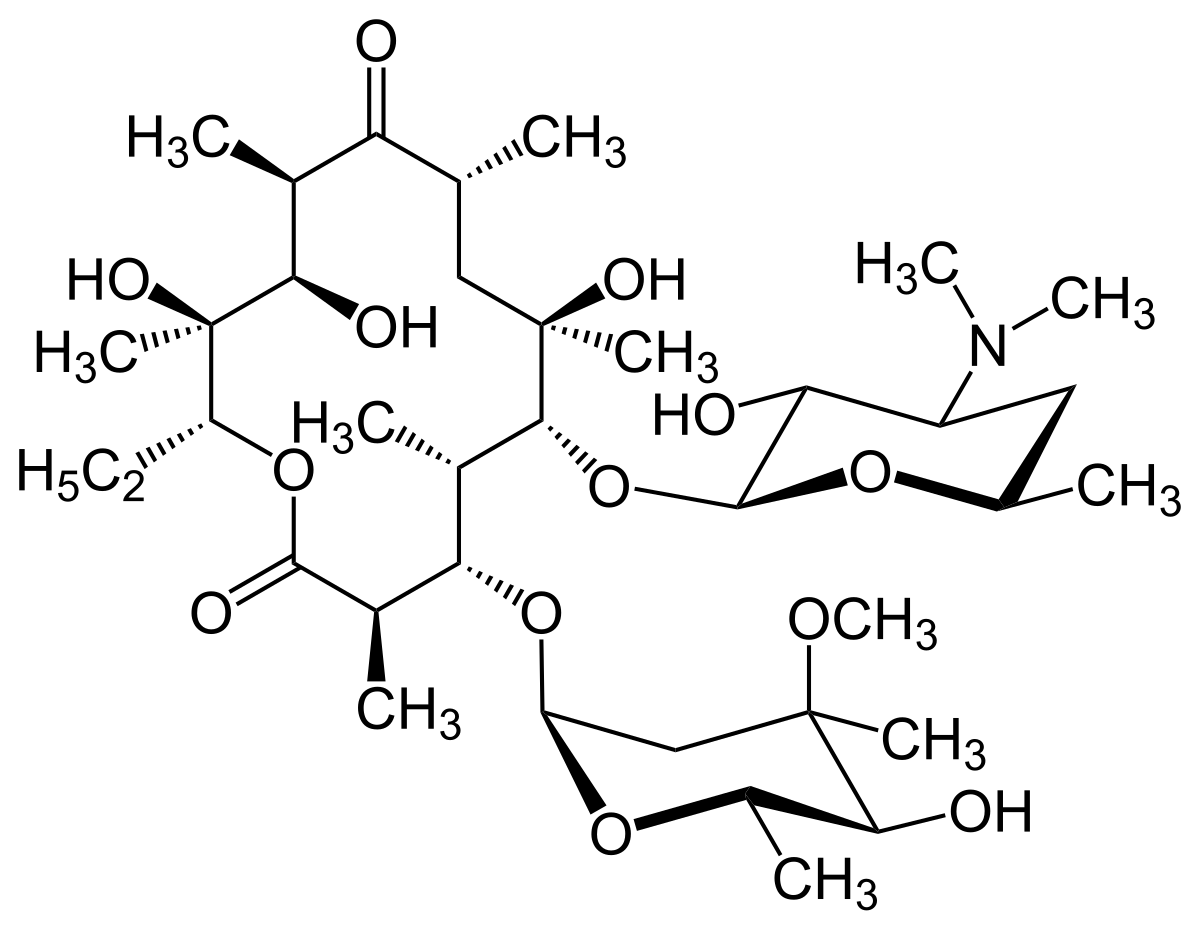



Macrolide Wikipedia




A Primary Structures Of 4 Acetyl Spiramycin And Download Scientific Diagram




08 7 Spiramycin Embonate Antibiotic 799 Espiramicin Foromacidin Il 5902 Nsc Provamycin Rp 5337 Rovamicina Rovamycin Rovamycine Selectomycin Sequamycin Spiramycins Stomamycin C H N O Trc




Structure Activity Relationships Of Ketolides Vs Macrolides Clinical Microbiology And Infection




Rcsb Pdb 1kd1 Co Crystal Structure Of Spiramycin Bound To The 50s Ribosomal Subunit Of Haloarcula Marismortui



Spiramycin New Drug Approvals
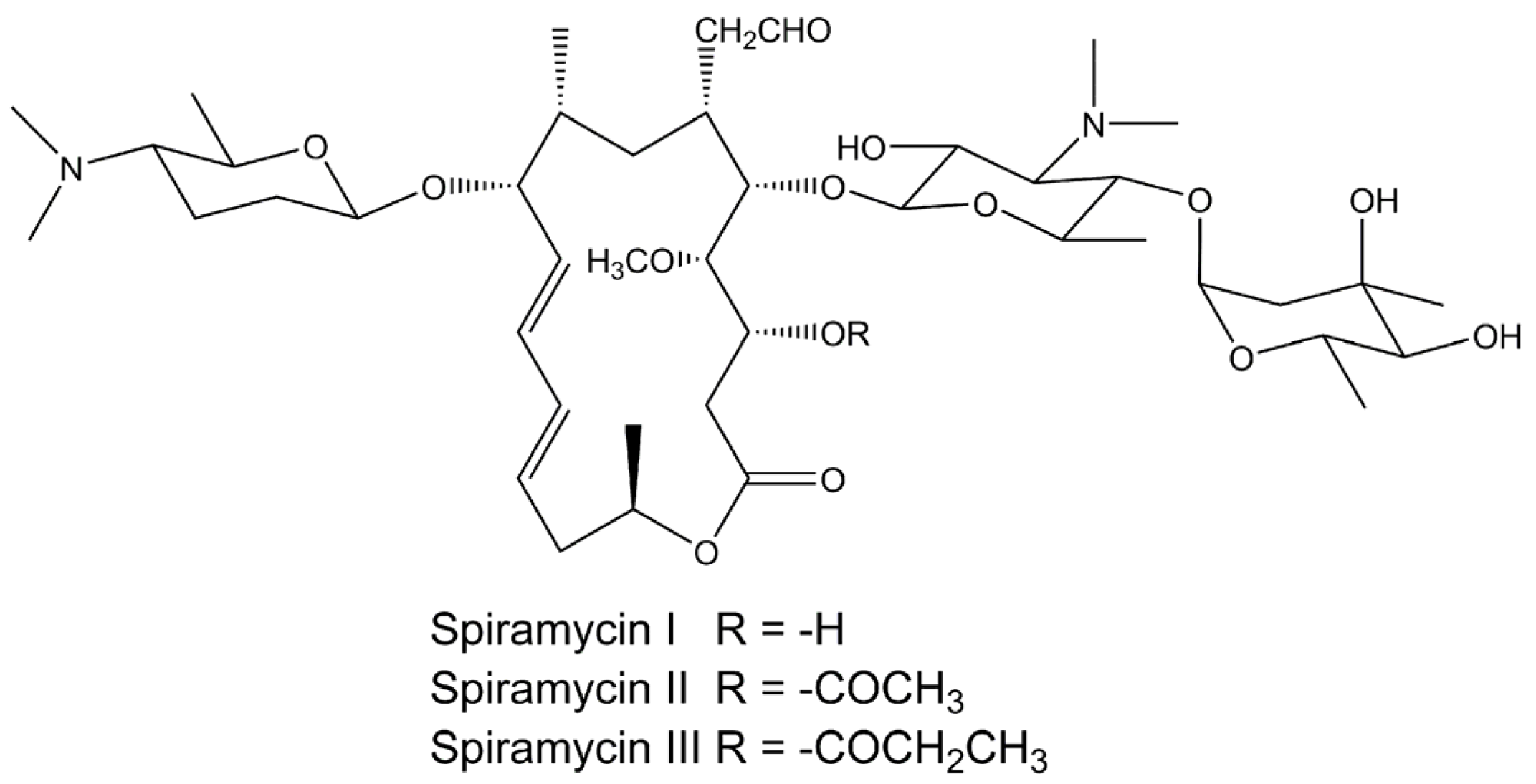



Applied Sciences Free Full Text Physicochemical Properties And In Vitro Dissolution Of Spiramycin Microparticles Using The Homogenate Antisolvent Precipitation Process Html




Spiramycin Rovamycine Macrolide Antibiotic Cas 8025 81 8 Ab Abcam




Simultaneous Multiresidue Determination Of Metronidazole And Spiramycin In Fish Muscle Using High Performance Liquid Chromatography With Uv Detection Sciencedirect
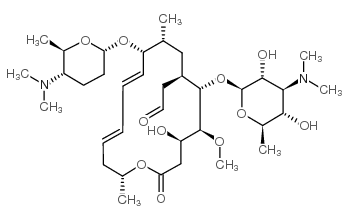



Neo Spiramycin I Cas 62 2 Chemsrc
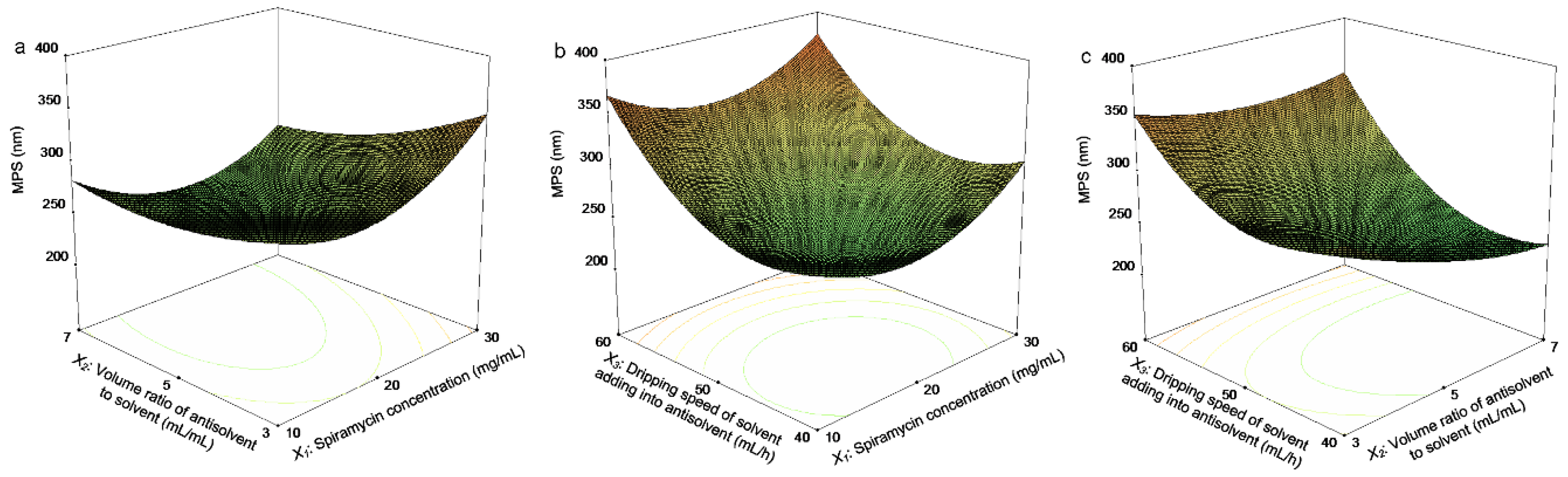



Applied Sciences Free Full Text Physicochemical Properties And In Vitro Dissolution Of Spiramycin Microparticles Using The Homogenate Antisolvent Precipitation Process Html




Polyamines Affect Diversely The Antibiotic Potency Journal Of Biological Chemistry
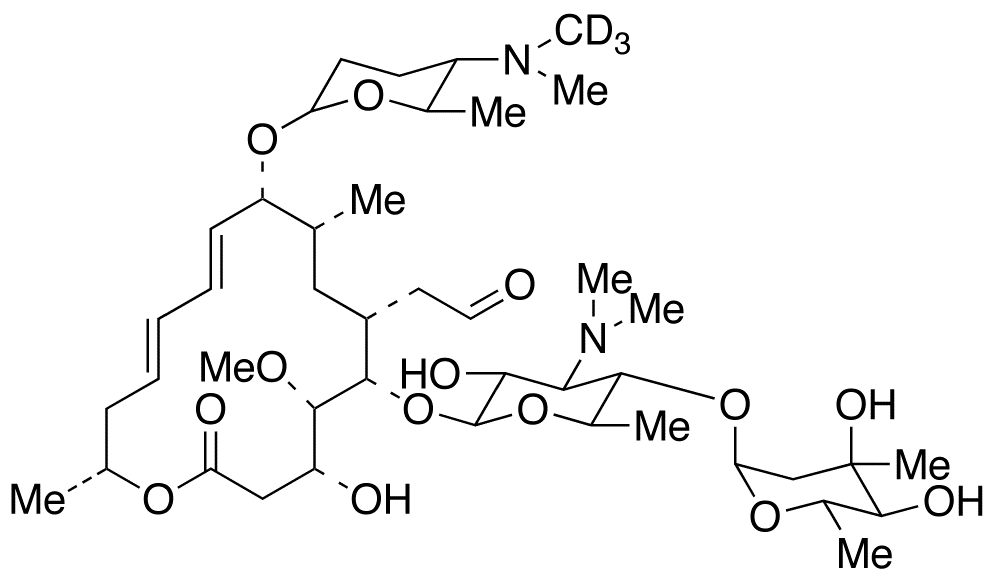



Spiramycin I D3 9 O 2r 5s 6r 5 Dimethylamino Tetrahydro 6 Methyl 2h Pyran 2 Yl Leucomycin V D3 Foromacidin A D3 Spiramycin A D3 C H D N O Trc




Spiramycin Adipate Cas 680 55 7 Antibiotic Medkoo
/4ECE7900D4445432802585F90081B95E/$file/FS44433_structure.png)



Spiramycin Adipate 680 55 7 Biosynth Carbosynth Product
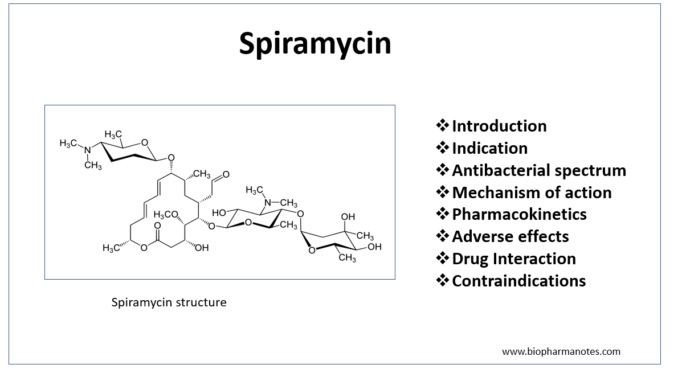



Pharmacology Of Spiromycin Biopharma Notes




Rcsb Pdb 1kd1 Co Crystal Structure Of Spiramycin Bound To The 50s Ribosomal Subunit Of Haloarcula Marismortui



Spiramycin Embonate C66h90n2o Pubchem




A Chemical Structure Of Spiramycin Pk 7 9 B Dose Dependent Download Scientific Diagram




Spiramycin Biorbyt




Efficient And Simple Hplc Method For Spiramycin Determination In Urine Samples And In Pharmaceutical Tablets Mahmoudi 18 Separation Science Plus Wiley Online Library




Spiramycin Goldbio



Spiramycin 99 Hplc Selleck Antibiotics Chemical




Spiramycin Structure C43h74n2o14 Over 100 Million Chemical Compounds Mol Instincts




Kegg Drug Spiramycin Adipate
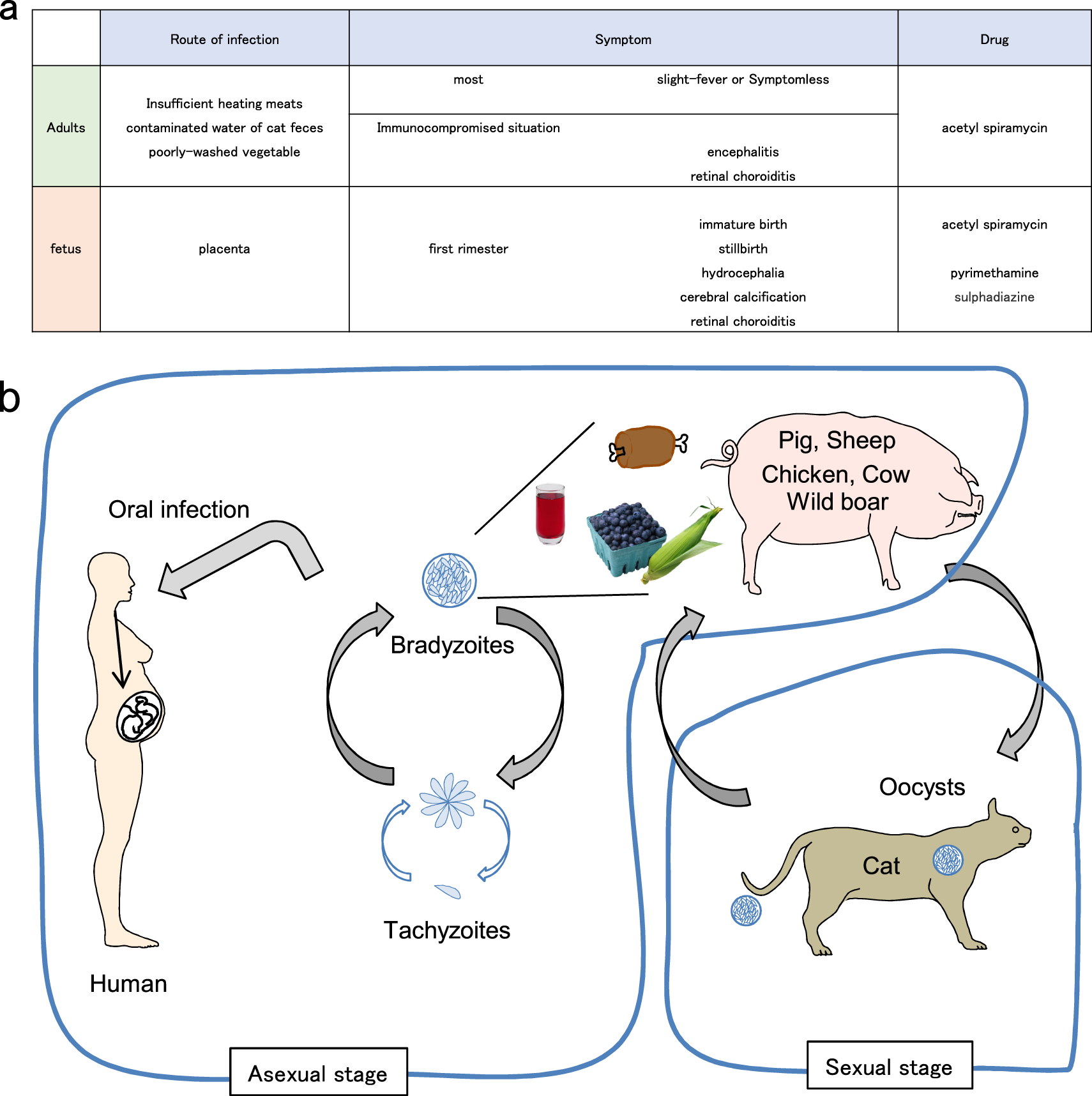



Innate Adaptive And Cell Autonomous Immunity Against Toxoplasma Gondii Infection Experimental Molecular Medicine




Neo Spiramycin I Cas 62 2 Glentham Life Sciences




Spiramycin 8025 81 8 Tci Europe N V
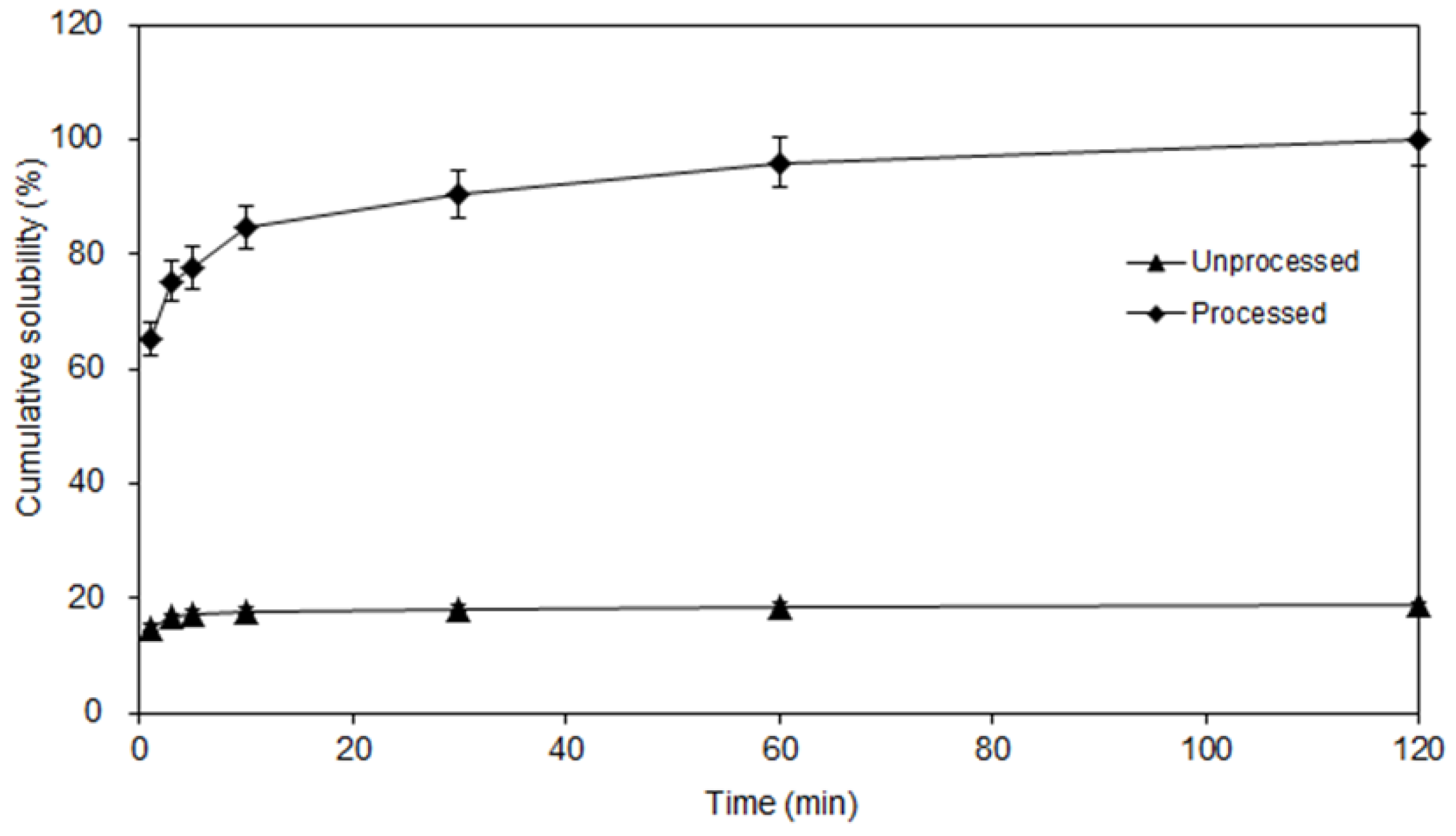



Applied Sciences Free Full Text Physicochemical Properties And In Vitro Dissolution Of Spiramycin Microparticles Using The Homogenate Antisolvent Precipitation Process Html
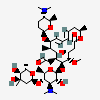



Spiramycin C43h74n2o14 Pubchem




Formacidine Absource Diagnostics




Spiramycin Biorbyt




Chemical Structures Of Main Components Of Spiramycin And Its Related Download Scientific Diagram




Spiramycin 90 0 Tci America Fisher Scientific
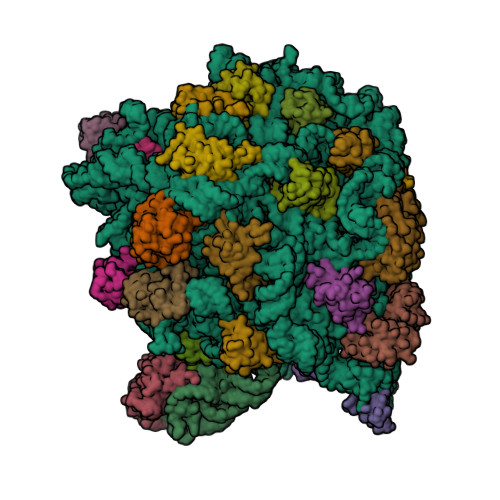



Rcsb Pdb 1kd1 Co Crystal Structure Of Spiramycin Bound To The 50s Ribosomal Subunit Of Haloarcula Marismortui




Market Forecasts And Industry Analysis Global Spiramycin Base Spiramycin Cas 8025 81 Joomag Newsstand




Structure Of Spiramycins And Genetic Organization Of The Spiramycin Download Scientific Diagram




680 55 7 Cas Msds Spiramycin Adipate Melting Point Boiling Point Density Cas Chemical Properties




Neo Spiramycin I D3 4a O De 2 6 Dideoxy 3 C Methyl A L Ribo Hexopyranosyl 9 O 2r 5s 6r 5 Dimethylamino Tetrahydro 6 Methyl 2h Pyran 2 Yl Leucomycin V D3 C H D N O Trc



The Evolution Of Substrate Discrimination In Macrolide Antibiotic Resistance Enzymes Nature Communications
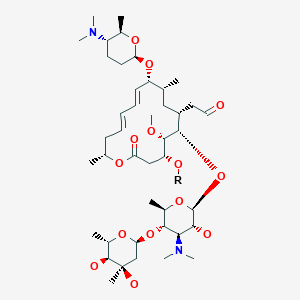



Spiramycin スピラマイシン New Drug Approvals
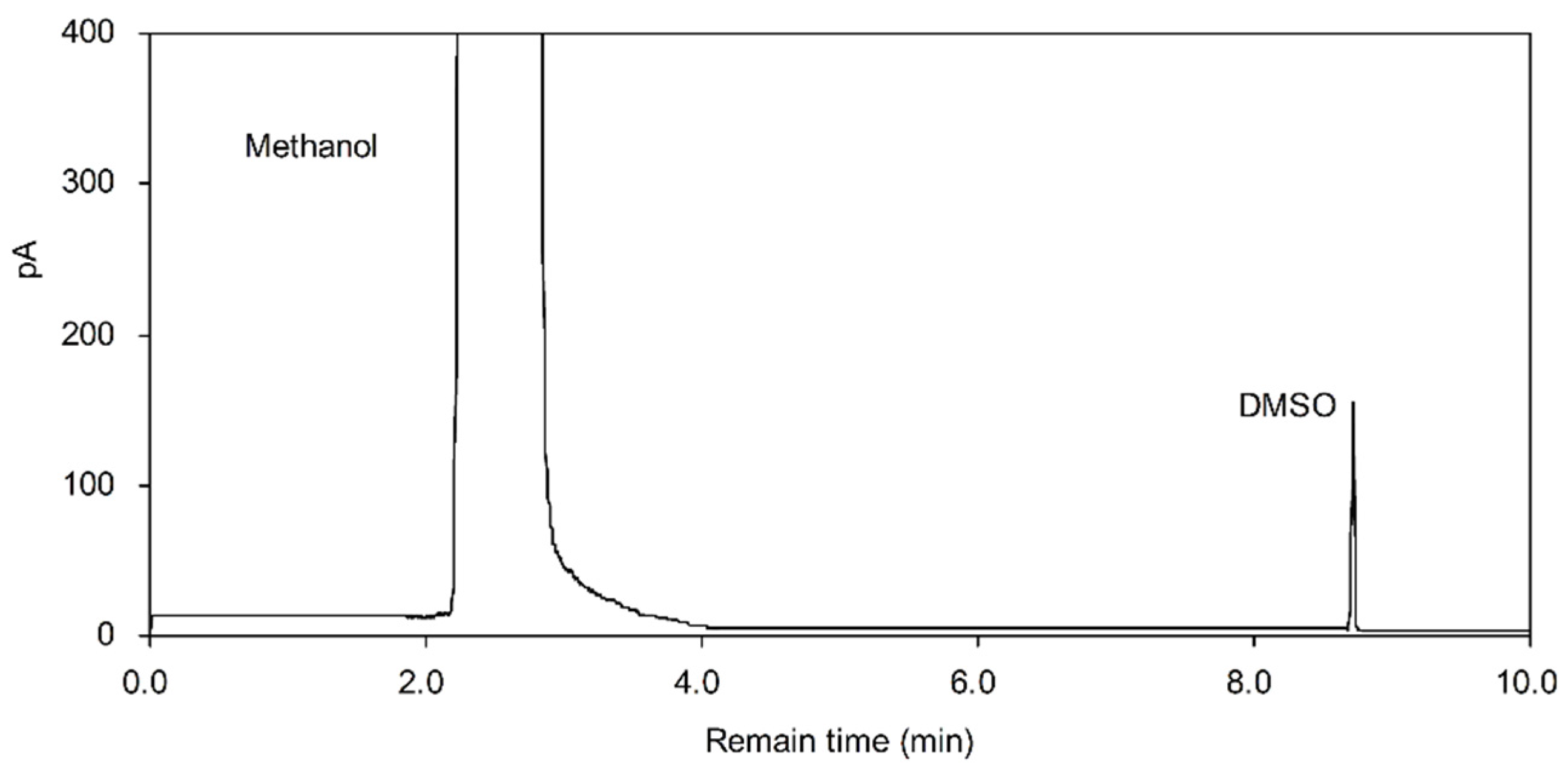



Applied Sciences Free Full Text Physicochemical Properties And In Vitro Dissolution Of Spiramycin Microparticles Using The Homogenate Antisolvent Precipitation Process Html




Figure 3 Application Of Different Analytical Techniques And Microbiological Assays For The Analysis Of Macrolide Antibiotics From Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms And Biological Matrices




Tylosin An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
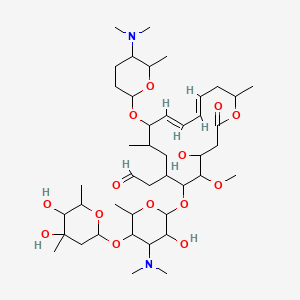



Spiramycin スピラマイシン New Drug Approvals




Spiramycin 8025 81 8




Acetyl Spiramycin Biochemical Mybiosource
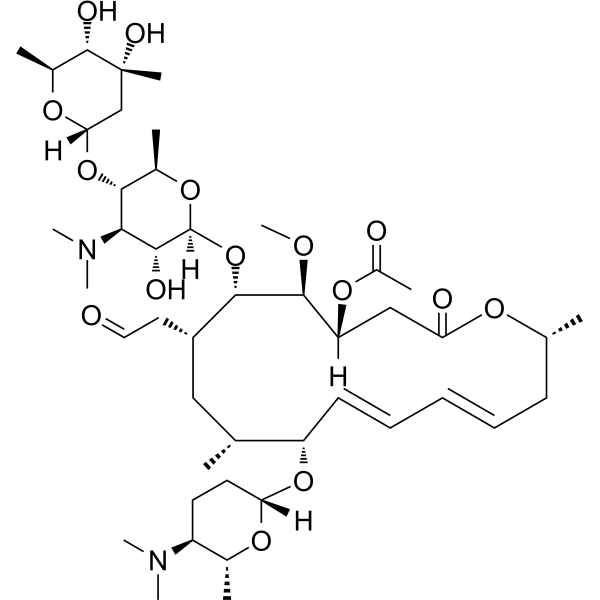



Acetylspiramycin Spiramycin B Macrolide Antibiotic Medchemexpress
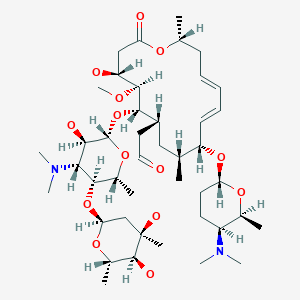



Spiramycin New Drug Approvals




Regulation Of The Biosynthesis Of The Macrolide Antibiotic Spiramycin In Streptomyces Ambofaciens Journal Of Bacteriology



Spiramycin Drug Monograph Druginfosys Com




Chemical Structure Of Obtained Spiramycin Derivatives Download Scientific Diagram



1



Fate Of Antibacterial Spiramycin In River Waters Springerlink


